Low temperature air to water heat pump is an efficient and cost-effective way to heat your home. It makes use of the warmth from the air round you to heat your home, even when the bloodless local weather temperature backyard is very low.
This effectivity kind of warmth pump is specially beneficial in wintry weather when the air temperature can drop to properly under zero. The warmth pump works by using drawing in bloodless air from outside, changing it to heat and then releasing the hot air into your home.

Introduction to low temperature air to water heat pump
Low temperature air to water warmness pumps are a kind of energy-efficient equipment that use ambient air or geothermal electricity to grant warmness for a swimming pool, home, or different warming application. LT warmth pumps are designed to furnish environment friendly warmth switch even at temperatures as low as -20°C. This technological know-how makes use of a refrigerant cycle and utilizes the outdoor air to furnish heating at some point of the wintry weather and cooling at some stage in the summer.
The basic working principle of a LT heat pump is the same as any other heat pump – it captures heat from the atmosphere and transfers it to a liquid medium, usually water. A compressor will be used to compress a refrigerant gas, and this gas will be passed through a condenser to dissipate the heat into the water. The water will then be circulated to the desired area for either heating or cooling. The compressor can then be used to draw in a low-temperature supply of air and circulate it back over the condenser for a second round of heat exchange.
The primary benefit of a LT heat pump is its efficiency and renewable sources of electrical energy cost savings. In addition, these systems require significantly less energy to operate than other traditional heating systems such as gas furnaces and electric boil.
Low temperature air to water heat pump price
Are you looking for a low temperature air to water heat pump for your home or business? If so, you may be wondering about the price.
The cost of a low temperature air to water heat pump can vary depending on several factors, such as the brand, model, and size. Generally, these types of heat pumps cost between $3,000 and $10,000. However, keep in mind that the installation costs can add to the total price.
It is important to consider the long-term savings that a heat pump can provide. While the upfront cost may seem high, a heat pump can save you money on your energy bills in the long run. Additionally, many states offer rebates and incentives for installing energy-efficient heating systems, which can help offset the cost.
When shopping for a low temperature air to water heat pump, be sure to research different brands and models to find one that fits your needs and budget. It may also be helpful to consult with a professional HVAC technician to determine the best heat pump for your specific situation.
Overall, the price of a low temperature air to water heat pump can vary, but it is an investment that can provide long-term savings and benefits.
Comparison of air source heat pump and ground source heat pump
An air source heat pump (ASHP) and a ground source heat pump (GSHP) are both renewable energy technologies that can be used to provide heating, cooling, and hot water for buildings. However, they differ in how they extract heat from the environment.
An ASHP extracts heat from the outdoor air using a refrigerant, which is compressed to increase its temperature and then circulated through a heat exchanger to provide heat to the building. On the other hand, a GSHP extracts heat from the ground using a loop of pipes buried in the ground, which contains a fluid that absorbs heat from the ground and carries it to a heat pump, where it is used to provide heat to the building.
One of the main advantages of ASHPs is that they are generally less expensive to install than GSHPs, as they do not require any excavation work. However, their efficiency decreases as the outdoor temperature drops, which means that they may need to be supplemented with another heating system during very cold weather. GSHPs, on the other hand, are generally more efficient than ASHPs, as the ground temperature remains relatively constant throughout the year. However, they are more expensive to install due to the excavation work required.
Another advantage of GSHPs is that they can also be used for cooling during the summer months, as the ground can be used as a heat sink to absorb heat from the building. ASHPs can also be used for cooling, but they are generally less efficient at this than GSHPs.
In terms of environmental impact, both ASHPs and GSHPs are considered to be environmentally friendly, as they use renewable energy to provide heating and hot water. However, the manufacturing process of the equipment and the refrigerants used in ASHPs can have a negative impact on the environment if they are not properly disposed of.
In conclusion, both ASHPs and GSHPs have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two will depend on a variety of factors, such as the climate, the size and location of the building, and the budget of the homeowner or developer. It is important to carefully consider these factors before making a decision on which system to install.
Low temperature air source heat pump installation points
When installing a low temperature air source heat pump, there are several key factors to consider to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Here are some installation points to keep in mind:
- Location: The heat pump should be installed in a location with adequate airflow and protection from extreme weather conditions. It should be placed on a stable surface that can support its weight.
- Insulation: Proper insulation is crucial for the heat pump to function efficiently. Ensure that the building is well-insulated to prevent heat loss.
- Piping: The piping connecting the heat pump to the building should be properly insulated to prevent heat loss and maintain energy efficiency.
- Groundwork: The ground on which the heat pump is installed should be levelled and compacted to prevent subsidence.
- Electrical supply: The heat pump requires a dedicated electrical supply to function properly. The electrical supply should be installed by a qualified electrician and meet the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Controls: The heat pump should be installed with appropriate controls to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. The controls should be installed by a qualified technician.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the heat pump is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Make sure that the heat pump is serviced by a qualified technician at least once a year.
Benefits of using Low Temperature Air to Water Heat Pump
- Cost Savings: Low temperature air to water heat pumps are designed to run at lower temperatures than traditional boilers, reducing energy costs and therefore saving you money.
- Increased Efficiency: This type of heat pump can transfer heat at a higher rate than traditional boilers, offering better performance and greater comfort.
- Low Maintenance and Longer Life Span: Low temperature air to water heat pumps require minimal maintenance and provide a very long life span.
- Ecology Benefits: Air-source heat pumps require no burning of fossil fuels and have virtually no greenhouse gas emissions.
- Quiet Operation: Low-temperature air source heat pumps are capable of running without making loud noises, unlike traditional boilers.
How Low Temperature Air to Water Heat Pump Works
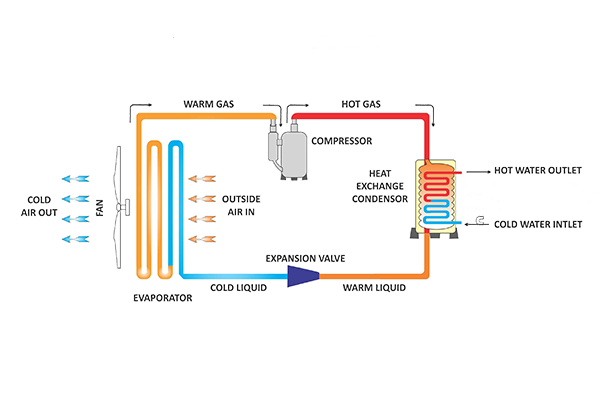
Low temperature air to water warmth pumps use air as its warmth supply and bloodless water as the sink. The technique starts offevolved with the aid of drawing in out of doors air via the out of doors unit the usage of a fan. The out of doors unit is geared up with a warmth exchanger, which absorbs the warmth from the air. The air is then surpassed over tubes containing the bloodless water, transferring the warmth from the air to the water. The warmth is then carried via a pipe with the aid of the heated water and delivered to the indoor unit.
The indoor unit transfers the heat to water and also distributes it through a pipe network, supplying the house and all other heating requirements. The cold water, which is now considerably colder, is then sent back to the outdoor unit to start the process again.
Low temperature air to water heat pumps are an excellent renewable energy-saving solution and are more efficient than other forms of heating. They are also more environmentally friendly, as no carbon emissions are created when they are used.
Best low temperature air to water heat pump for home use
If you are looking for an efficient way to heat your home, a low temperature air to water heat pump is an excellent option. Here are some of the best models available for home use:
1. GOMON
The GOMON is a reliable and efficient air to water heat pump that can operate at temperatures as low as -15°C. It is available in a range of sizes to suit different homes and has a COP (coefficient of performance) of up to 4.5, making it one of the most efficient models on the market.
2. Daikin Altherma
The Daikin Altherma is another excellent air to water heat pump that is suitable for low temperature operation. It has a COP of up to 4.6 and can operate at temperatures as low as -25°C. The Daikin Altherma is available in a range of sizes and can be used for both heating and hot water.
3. NIBE F2040
The NIBE F2040 is a high-performance air to water heat pump that can operate at temperatures as low as -20°C. It has a COP of up to 4.7 and is available in a range of sizes to suit different homes. The NIBE F2040 also has a built-in control system that allows you to monitor and adjust the temperature and other settings remotely.
4. Vaillant aroTHERM plus
The Vaillant aroTHERM plus is a versatile air to water heat pump that can operate at temperatures as low as -20°C. It has a COP of up to 4.5 and is available in a range of sizes to suit different homes. The Vaillant aroTHERM plus also has a built-in weather compensation system that adjusts the temperature based on the outside temperature.
These are just a few of the best low temperature air to water heat pumps available for home use. When choosing a heat pump, consider the size of your home, your budget, and the climate in your area. With the right heat pump, you can enjoy efficient and cost-effective heating all year round.
Different Types of Low Temperature Air to Water Heat Pumps
:
- Ground Source Heat Pump – A Ground Source Heat Pump is a system that extracts and collects geothermal energy from the ground for heating and cooling purposes. Heat pumps with this type of system use loops of buried pipes known as ground loops to transfer thermal energy from the ground to the building.
- Water Source Heat Pump – A Water Source Heat Pump uses a water-based system as the source for heating and cooling. The unit draws heat from a pond, lake, river or other water source, circulates the heat through the system and distributes it to the desired areas.
- Air-to-Water Heat Pump – An Air-to-Water Heat Pump pulls heat from the outside air and then distributes it through the home’s water system. This is usually used when no other sustainable source of energy such as ground source or water source is available.
- Hybrid Heat Pump – A Hybrid Heat Pump is a combination of a heat pump and traditional air source air conditioning system. The heat pump works as the primary source of heat, while the air conditioning system works as a supplement when the heat pump is unable to meet the home’s heating demand.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting for Low Temperature Air to Water Heat Pumps
- Inspect the Electrical System
The electrical system should be inspected and tested conform to national safety standards. Make sure all parts, such as switches, power cord and connections, are free of defects and damage. Check the operation of the thermostat, and make sure the electrical wiring is in good condition.
- Inspect the Refrigerant System
The refrigerant system should be inspected regularly. Check the pressure in the evaporator, condenser, and suction lines. Check that the system is operating at the proper pressure and temperature. Make sure the expansion valve is adjusted correctly, as this has a significant impact on the performance of the heat pump.
- Check the Heat Flow Rate
The heat flow rate should be checked regularly to ensure the system is operating at optimal efficiency. The system should be tested for air and water temperatures
You may like:

